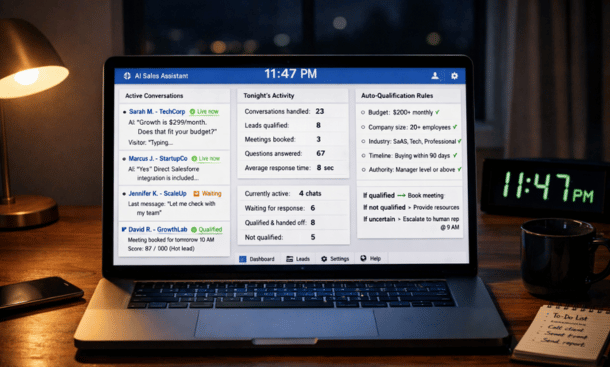
Sales assistants powered by AI handle the initial conversations that most reps find tedious but absolutely critical for pipeline health. These digital assistants engage prospects through chat, voice, or email to answer basic questions, gather qualifying information, and schedule meetings with your human team. The transformation happens when leads get instant responses at 2am on Sunday instead of waiting until Monday morning when they’ve already moved on to a competitor. Response speed alone can increase conversion rates by 30 to 40 percent, and that’s before accounting for the consistency and qualification accuracy AI brings to every interaction. To understand where AI assistants fit in your automation strategy, our guide on automating sales processes with AI provides the complete framework from prospecting through close.
The economics of immediate response
Research consistently shows that the odds of qualifying a lead drop by over 80 percent if you wait longer than five minutes to respond. Yet most sales teams take hours or even days to follow up with new inquiries because reps are in meetings, handling other prospects, or offline entirely.
This creates a mathematical problem. You spend money on marketing to generate leads, those leads express interest by filling out forms or requesting information, then you squander that interest by making them wait. The leads who were genuinely curious move on to faster competitors. The only people left when you finally respond are those desperate enough to wait, which often correlates with challenging customers or weak buying intent.
AI sales assistants eliminate wait time completely. A prospect submits a contact form at 11pm on Saturday, and the assistant engages them immediately with relevant questions and information. By the time your human team arrives Monday morning, the assistant has already qualified the lead, answered their initial questions, and either scheduled a meeting or determined they’re not a fit.
The compound effect shows up across your entire funnel. More leads get engaged before interest fades. Qualification happens faster so your human reps spend time exclusively on prospects who meet your criteria. Meeting schedules fill up with better-fit opportunities because the assistant handles the initial filtering that used to consume hours of rep time.
What AI assistants actually do
These tools handle several distinct functions that previously required human attention. Initial engagement responds to inbound inquiries with contextually relevant information based on how the prospect found you and what page they were viewing. Someone visiting your enterprise pricing page gets different initial questions than someone downloading an introductory guide.
Qualification conversations gather the information your sales team needs to determine fit and priority. The assistant asks about company size, current challenges, budget timeline, decision-making process, and other qualifying factors. It does this through natural conversation rather than feeling like an interrogation.
Objection handling addresses common concerns without escalating to humans unnecessarily. When prospects ask about pricing, integrations, implementation time, or other frequently asked questions, the assistant provides accurate answers drawn from your knowledge base. It recognizes when questions exceed its capability and routes those to humans appropriately.
Meeting scheduling coordinates calendars to find mutually available times and sends confirmations with all necessary details. Advanced assistants can even reschedule when conflicts arise, sending the prospect new options without involving your rep. This alone saves 20 to 30 minutes per booked meeting that reps previously spent on coordination emails.
Lead nurturing continues the relationship with prospects who aren’t ready to buy immediately. The assistant checks in periodically with relevant content, answers new questions as they arise, and monitors engagement signals that indicate increased buying intent. When a nurtured lead heats up, it gets routed back to sales automatically.
Voice vs chat vs email assistants
Different AI assistant modalities work better for different sales contexts. Chat assistants embedded on your website capture visitors while they’re actively browsing and interested. They’re perfect for inbound lead generation where people are researching solutions and want immediate answers.
The conversational nature of chat feels less committal than filling out a long contact form. Prospects will engage with a chat assistant to get quick answers even if they’re not ready to talk to sales. This lowers the barrier to engagement and captures earlier-stage interest that you can nurture over time.
Voice assistants handle phone inquiries and can even make outbound calls for initial contact or follow-up. They’re particularly valuable for high-volume, transactional sales where the qualifying questions are straightforward and prospects expect phone contact. Industries like real estate, insurance, and home services benefit significantly from voice AI.
Email assistants manage inbox conversations, responding to inquiries that come through email channels. They’re essential for B2B contexts where email remains the dominant communication channel. The assistant monitors your sales inbox, categorizes incoming messages, and either responds directly or routes to appropriate team members with context.
Most businesses ultimately use a combination. Your website chat assistant captures inbound interest, an email assistant handles follow-up conversations, and a voice assistant calls prospects who prefer phone contact. The key is making transitions between these channels seamless so prospects don’t have to repeat information.
Training your assistant to sound like your brand
Generic AI assistants feel robotic and impersonal because they use vanilla language that could apply to any business. Effective assistants reflect your brand voice and adapt their communication style to match how your team actually talks to prospects.
Start by documenting your brand voice guidelines. Are you formal and consultative, or casual and friendly? Do you use industry jargon or explain things in plain language? Should the assistant use humor or stay strictly professional? These decisions shape how the AI interacts with every prospect.
Feed the assistant examples of great conversations from your top sales reps. Let it analyze the language patterns, question styles, and rapport-building techniques that work for your business. The AI learns from these examples to mimic effective approaches rather than relying on generic templates.
Define explicit boundaries for what the assistant should and shouldn’t handle. Complex pricing discussions that require customization should route to humans. Technical questions that involve nuanced product details beyond the knowledge base need escalation. The assistant should recognize its limitations and hand off gracefully rather than providing incomplete or incorrect information.
Test extensively before full deployment. Have team members, friends, and even beta customers chat with your assistant and provide feedback. Does it feel helpful or annoying? Does the personality match your brand? Are responses accurate and relevant? This testing reveals gaps in training that you can fix before prospects encounter them.
Handling the human handoff smoothly
The transition from AI assistant to human rep is where many implementations break down. Prospects get frustrated when they have to repeat information they already provided to the assistant. Reps waste time reviewing conversation history to understand context before engaging.
Seamless handoffs require the assistant to summarize qualification information and conversation history for the human rep. When a meeting gets scheduled, the rep should receive a briefing with the prospect’s key challenges, budget expectations, timeline, and any specific questions they asked. This lets reps jump into productive conversations instead of starting from scratch.
Set clear expectations with prospects about when they’re talking to AI versus humans. Transparency builds trust. The assistant can say something like “I’m an AI assistant helping to answer initial questions and find a time for you to speak with our team. I’ll make sure they have all the context from our conversation.” This manages expectations without feeling apologetic about using automation.
Create escalation triggers that move conversations to humans at the right moments. When a prospect expresses frustration, asks complex questions multiple times, or exhibits strong buying signals, the assistant should recognize these situations and offer to connect them with a person immediately. “I want to make sure you get the detailed answer you need. Let me connect you with someone from our team who can help right away.”
Common mistakes that sabotage assistant effectiveness
Over-automating the conversation creates frustrating experiences where prospects feel trapped talking to a bot when they want human help. Your assistant should make it easy to reach a person at any point. Including a clear “talk to a human” option in every interaction prevents frustration from building.
Under-training the assistant on your specific business leads to generic, unhelpful responses that don’t address prospect questions accurately. You can’t just flip on a generic chatbot and expect good results. The assistant needs comprehensive training on your products, processes, pricing, and positioning to provide value.
Ignoring negative feedback signals like high abandonment rates or lots of “I want to talk to a person” requests indicates something is wrong with the experience. Monitor these metrics closely during the first few weeks and make adjustments. If prospects consistently bail out of conversations at specific points, that’s where your assistant needs improvement.
Failing to update the assistant as your business evolves creates accuracy problems. When you launch new products, change pricing, or update policies, the assistant needs to learn these changes immediately. Stale information damages credibility and creates cleanup work for your human team when prospects get outdated details.
Measuring success purely on automation rates misses the point. The goal isn’t to minimize human conversations, it’s to maximize qualified pipeline. An assistant that automates 80 percent of conversations but generates low-quality leads is worse than one that routes 50 percent to humans but those conversations turn into deals. Focus on downstream metrics like meeting show rates, opportunity creation, and closed revenue attributed to assistant-qualified leads.
Integration with your existing sales stack
AI assistants create the most value when they connect to your CRM, calendar, marketing automation, and other sales tools. This integration ensures information flows bidirectionally rather than creating data silos.
CRM integration automatically creates or updates contact records when prospects engage with your assistant. Qualification information gets logged as custom fields, conversation transcripts attach to contact records, and meeting bookings appear as activities. Your reps see complete context without manually transferring information.
Calendar integration lets the assistant access real-time availability for your entire team and book meetings directly. More sophisticated setups can route prospects to specific reps based on territory, expertise, or current workload. The assistant balances calendars automatically rather than clustering all meetings with whoever happens to be listed first.
Marketing automation connections ensure prospects who aren’t sales-ready get added to appropriate nurture campaigns. Someone who’s researching but not ready to buy for six months shouldn’t just disappear. The assistant adds them to a drip campaign that provides ongoing value until their timeline accelerates.
Most platforms support these integrations through native connections or via tools like Zapier. Budget extra time for setup and testing because integration issues cause the most common implementation headaches. Data mapping needs to be precise, error handling needs to work correctly, and you need fallback processes when systems go down.
Building an effective AI sales assistant takes planning and iteration, but the payoff in faster response times, consistent qualification, and freed-up rep capacity makes it one of the highest-impact sales automations available. Once your assistant is qualifying leads and booking meetings, you need visibility into whether all this automation is actually improving your bottom line. Our guide on sales automation metrics shows you exactly which numbers to track and how to calculate ROI on your automation investments.