Table of Contents
- Why Industry-Specific Customization Matters
- Tech and SaaS Company Customizations
- Retail and E-Commerce Customizations
- Manufacturing and Distribution Customizations
- Cross-Industry Customization Patterns
- Choosing the Right Customizations for Your Vertical
- Implementation Considerations by Industry
- Building Your Industry-Specific Strategy
Not all businesses need the same ERP customizations—a SaaS startup in San Francisco has totally different needs than a manufacturing plant in San Diego. Industry-specific customization addresses the unique workflows, compliance requirements, and operational challenges of your particular sector. Tech companies might prioritize agile project tracking and API integrations, while retailers focus on omnichannel inventory and POS connections. Getting this right means understanding how to tailor your system to your business vertical, not just your company size. I’ll show you exactly what customizations matter most for tech, retail, and manufacturing operations.
Why Industry-Specific Customization Matters
Generic ERP systems are built for the broadest possible market, which means they try to be everything to everyone. That approach creates gaps when you operate in a specific industry with unique requirements that general-purpose software doesn’t address.
Each industry has its own operational DNA. The way a software company manages projects bears little resemblance to how a clothing retailer manages inventory, which is completely different from how a manufacturer manages production schedules. These aren’t just minor variations—they’re fundamental differences in business models, workflows, and success metrics.
Industry-specific regulations create customization needs that businesses in other sectors don’t face. Food distributors need lot tracking and temperature monitoring that tech companies never think about. Healthcare providers need HIPAA compliance features that manufacturers don’t require. Financial services firms face regulatory reporting that retailers can ignore.
Competitive dynamics vary dramatically by industry. In fast-fashion retail, speed to market is everything, so customizations that accelerate design-to-shelf cycles create competitive advantage. In contract manufacturing, quality control and traceability matter most, so customizations enabling detailed tracking and compliance documentation deliver value. Understanding what drives success in your industry guides smart customization choices.
Customer expectations differ by industry in ways that impact ERP requirements. E-commerce customers expect real-time inventory visibility and order tracking, driving integration customizations. B2B manufacturing customers might need custom portals for submitting specifications and tracking production progress. Professional services clients expect detailed project transparency and billing breakdowns.
The scale and complexity of transactions varies widely. A SaaS company might process thousands of small recurring transactions monthly. A manufacturing firm might have dozens of complex multi-line purchase orders with intricate specifications. A retail chain processes enormous transaction volumes at relatively low values. These patterns drive different customization needs around performance, automation, and data handling.
Industry-specific customization isn’t about adding bells and whistles—it’s about making your ERP understand the language of your business. When your system thinks like your industry operates, everything from training to daily operations becomes dramatically easier.
Tech and SaaS Company Customizations
Technology companies and SaaS businesses have unique ERP requirements driven by their business models, development processes, and customer relationships.
Subscription revenue management is probably the most critical customization area for SaaS companies. Standard ERP systems handle one-time sales well but struggle with recurring revenue, usage-based billing, tiered pricing, and complex subscription modifications. Custom billing engines calculate monthly recurring revenue correctly, handle prorations when customers upgrade mid-cycle, manage trial periods and grace periods, and automate renewal processes.
Project management customizations support agile development workflows that traditional project accounting doesn’t handle well. Tech companies need sprint planning integrated with resource allocation, time tracking that maps to stories and epics rather than just projects, and burndown charts that connect development work to financial performance. Custom dashboards show velocity metrics, feature completion rates, and project profitability in ways meaningful to development teams.
API and integration capabilities matter enormously for tech companies whose products often require connecting multiple systems. Custom integration frameworks let your ERP communicate with development tools like GitHub and Jira, customer success platforms like Gainsight, and analytics tools like Mixpanel. These integrations surface operational data in your ERP for holistic business visibility.
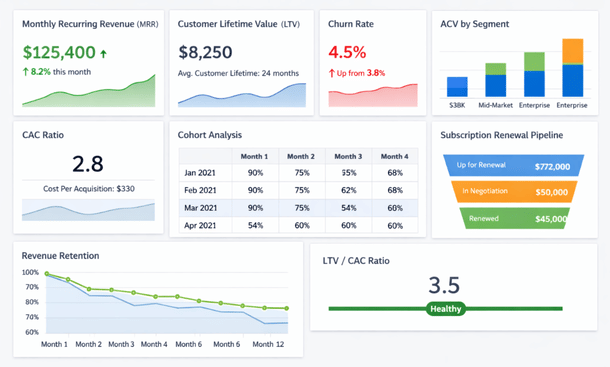
Customer success tracking connects operational metrics with financial data. Customizations that link product usage data to customer accounts help identify expansion opportunities and churn risks. When your ERP knows that a customer’s usage dropped thirty percent this quarter, your customer success team can intervene before renewal time.
Revenue recognition customizations handle complex accounting requirements for software companies. Multi-element arrangements, where customers buy software plus services plus support, require sophisticated allocation of transaction prices. Performance obligations, revenue deferral schedules, and contract modifications all need proper handling per ASC 606 and IFRS 15 standards.
Equity and stock option management is critical for startups and growing tech companies. Custom modules track option grants, vesting schedules, exercise activity, and dilution modeling. Integration with cap table management keeps ownership structure synchronized with financial reporting.
Headcount planning and hiring pipeline tracking connects HR processes with financial planning. Tech companies growing rapidly need to see how open positions, recruiting pipeline, and expected hire dates impact cash burn and runway. Custom reports project staffing costs and help manage growth within budget constraints.
Multi-currency and international operations support matters for tech companies serving global markets. Customizations handle billing customers in their local currency, managing foreign exchange exposure, and consolidating international entities for reporting. Transfer pricing and international tax considerations require specialized functionality.
Retail and E-Commerce Customizations
Retail businesses face completely different challenges that drive their own set of critical customizations.
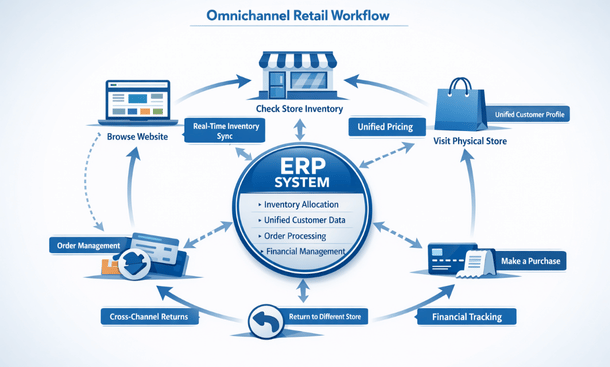
Omnichannel inventory management is fundamental for modern retailers. Customers expect to buy online and pick up in store, return online purchases to physical locations, or check in-store availability before visiting. Custom inventory allocation logic reserves stock appropriately across channels, prevents overselling when the same item appears in multiple places, and provides accurate availability across all touchpoints.
Point of sale integration connects your physical store systems with your ERP. Real-time transaction sync ensures every sale immediately updates inventory, customer purchase history, and financial records. Return processing in stores needs to properly credit customers and return inventory to available stock. Employee discounts, gift cards, and loyalty programs require proper system support.
Size and color matrix management handles product variants efficiently. A t-shirt in five colors and six sizes creates thirty SKUs that need coordinated management. Customizations let buyers manage inventory at the style level while tracking individual SKUs, generate purchase orders that consider total style needs, and create reports showing performance by attribute rather than requiring analysis across dozens of individual SKUs.
Seasonal planning and merchandise assortment customizations help retailers prepare for buying cycles. Tools for open-to-buy management ensure purchasing stays within budget while maintaining appropriate inventory levels. Pre-season planning allocates budgets across categories, tracks actual spending against plans, and flags when buyers are over or under-spending.
Vendor and supplier collaboration portals let your suppliers access relevant information directly. Vendors can view purchase orders, update expected ship dates, submit invoices electronically, and access product specifications. This transparency reduces email back-and-forth and speeds up procurement cycles.
Promotion and markdown management tracks the financial impact of sales, clearance events, and promotional pricing. Customizations calculate true margins after promotions, help plan markdown strategies to clear seasonal merchandise, and analyze which promotional tactics drive the best returns.
Drop ship and vendor direct fulfillment handles scenarios where you sell products but never physically touch inventory. The ERP needs to track these transactions differently—revenue is recognized but inventory never enters your system. Purchase orders automatically route to vendors when customers place orders for drop-ship items.
Store clustering and allocation customizations help multi-location retailers distribute inventory intelligently. Stores in different regions or with different customer demographics need different product mixes. Allocation rules push new inventory to appropriate stores based on historical performance, demographics, and store attributes.
Rental and subscription models for retail require specialized handling. Furniture rental companies, tool libraries, or clothing subscription services need to track individual item status, rental agreements, return processing, and item condition. Standard sale transactions don’t capture the complexity of these business models.
Manufacturing and Distribution Customizations
Manufacturing operations have perhaps the most specialized ERP requirements given the complexity of production processes, supply chains, and quality standards.
Bill of materials and recipe management goes far beyond simple component lists. Multi-level BOMs show assemblies within assemblies within finished goods. Alternate BOMs handle situations where different component versions work depending on availability. Formula-based quantities calculate required materials based on batch sizes rather than fixed amounts.
Production scheduling and capacity planning customizations optimize manufacturing operations. Finite capacity scheduling considers actual machine and labor availability rather than assuming infinite capacity. Customizations factor in setup times, changeover requirements, and maintenance windows. Visual scheduling boards let production planners drag and drop jobs to optimize throughput.
Quality management systems ensure products meet specifications. Custom workflows route products through inspection stations, record test results and measurements, and hold or release lots based on pass/fail criteria. Statistical process control tracks metrics over time and flags when processes drift out of tolerance. Non-conformance tracking documents issues, root cause analysis, and corrective actions.
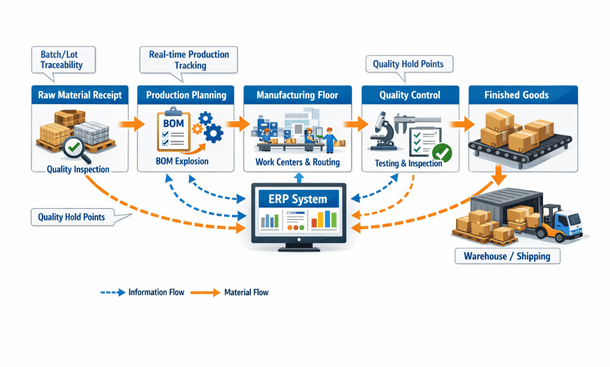
Lot and serial number traceability provides visibility from raw materials through finished goods and customer delivery. Complete traceability lets you answer questions like “which finished goods contain material from lot X” or “trace this serial number back to all components and their suppliers.” This capability is essential for recalls, quality investigations, and regulatory compliance.
Work order and job costing customizations track actual production costs against standards. Capture labor hours, material consumption, machine time, and overhead allocation at the work order level. Variance analysis shows where actual costs deviate from standards, highlighting opportunities for efficiency improvements.
Supply chain visibility and vendor scorecarding help manage complex supplier relationships. Track on-time delivery rates, quality metrics, and lead time performance for each vendor. Automated alerts flag when vendor performance deteriorates. Preferred supplier programs give best performers favorable terms and increased volume.
Equipment maintenance management prevents unplanned downtime. Preventive maintenance schedules trigger work orders based on runtime hours, production counts, or calendar intervals. Maintenance history tracking helps predict equipment failures. Integration with production scheduling ensures maintenance happens during planned downtime rather than disrupting production.
Waste and scrap tracking captures material losses throughout production. Different scrap types—setup waste, in-process defects, packaging trim—need separate tracking for analysis. Customizations calculate scrap rates, trend performance over time, and flag anomalies requiring investigation.
Make-to-order and engineer-to-order capabilities support custom manufacturing. Configure-price-quote tools let sales teams price custom products using rules and parameters. Engineering change management controls how product designs evolve while maintaining traceability of which changes affect which orders.
Regulatory compliance and certification tracking manages industry-specific requirements. FDA-regulated manufacturers need 21 CFR Part 11 compliance for electronic records. Aerospace manufacturers track certifications and test data. Medical device makers maintain design history files. These specialized requirements drive deep customizations.
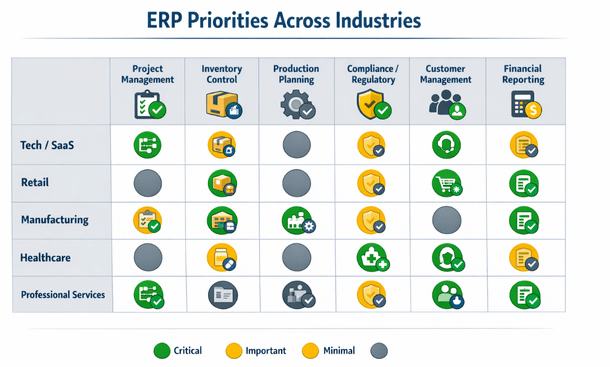
Cross-Industry Customization Patterns
While each industry has unique needs, some customization patterns appear across multiple sectors with industry-specific variations.
Advanced financial reporting customizations appear in every industry but with different focuses. Tech companies need detailed deferred revenue schedules. Retailers need margin analysis by category and location. Manufacturers need job costing and work-in-process reporting. The underlying need—better financial visibility—is universal, but implementations vary dramatically.
Customer portal customizations let clients access relevant information self-service. Tech companies provide product documentation and support tickets. Retailers show order history and tracking. Manufacturers give customers visibility into production status and quality certificates. The portal concept is cross-industry, but content and features are sector-specific.
Mobile access enables field work across industries. Retail store managers conduct cycle counts on tablets. Manufacturing quality inspectors record results on the factory floor. Service technicians access customer information and record time at job sites. Mobile customization requirements depend entirely on what work happens outside the office.
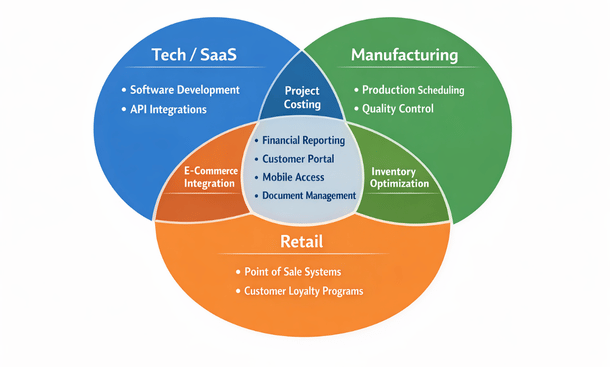
Document management systems organize files across all industries. Tech companies store product specifications and technical documentation. Retailers manage vendor catalogs and style guides. Manufacturers maintain certifications, test results, and quality documentation. Everyone needs to attach relevant documents to records and ensure version control.
Approval workflow automation delivers value regardless of industry. Purchase requisition approvals, expense report sign-offs, credit limit increases, and price override authorizations follow similar patterns. Industry-specific nuances appear in what requires approval and who approves it, but the workflow mechanics are comparable.
Business intelligence and analytics customizations help every business understand performance. Key performance indicators differ dramatically by industry—SaaS companies track MRR and churn while manufacturers monitor OEE and cycle time—but the need for custom analytics dashboards is universal.
The pattern to recognize is that customization categories apply across industries while specific implementations remain highly sector-focused. Understanding both the universal patterns and industry-specific requirements helps you learn from best practices in other sectors while ensuring customizations fit your unique operational reality.
Choosing the Right Customizations for Your Vertical
With so many possible industry-specific customizations, how do you prioritize which ones matter most for your business?
Start by identifying your industry’s critical success factors. What operational capabilities determine whether businesses in your sector win or lose? For SaaS companies, it’s often customer acquisition and retention efficiency. For retailers, inventory turnover and margin management. For manufacturers, production efficiency and quality consistency. Prioritize customizations that directly impact your critical success factors.
Analyze your competitive positioning within your industry. If you compete on price, customizations that reduce operational costs deserve priority. If you compete on speed, focus on customizations that accelerate processes. If you compete on quality, invest in quality management and compliance customizations. Your competitive strategy should guide customization decisions.
Consider regulatory and compliance requirements specific to your industry. These aren’t optional—you need customizations that keep you compliant regardless of other priorities. Food manufacturers need FDA traceability. Public companies need SOX compliance controls. Exporters need export documentation and compliance screening. Map your regulatory landscape before planning discretionary customizations.
Talk to peers in your industry about their ERP implementations. Industry associations, conferences, and professional networks provide opportunities to learn what customizations delivered value for similar businesses. While every company is unique, businesses in the same industry face remarkably similar challenges.
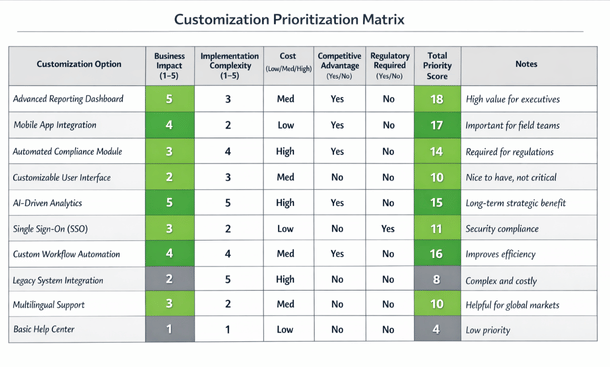
Evaluate vendor and partner expertise in your industry. Implementation partners who specialize in your sector bring pre-built customizations, best practices, and industry knowledge that generic consultants lack. The premium you pay for industry expertise often delivers better results than trying to educate generalists about your business.
Look at industry-specific ERP solutions as alternatives to customizing general-purpose systems. Vertical ERPs designed for specific industries often include as standard features what you’d need to customize in generic systems. The trade-off is potentially higher software costs but lower customization and maintenance expenses.
Phase customizations over time based on maturity and readiness. Some customizations make sense only after you’ve mastered basics. Manufacturers might start with basic production tracking before adding sophisticated scheduling optimization. Retailers might implement core POS integration before tackling advanced allocation algorithms.
Be honest about your organization’s capability to use sophisticated customizations. Building advanced analytics is worthless if your team won’t use them for decision-making. Implementing complex automation fails if your processes aren’t standardized enough to automate. Match customization sophistication to organizational maturity.
Implementation Considerations by Industry
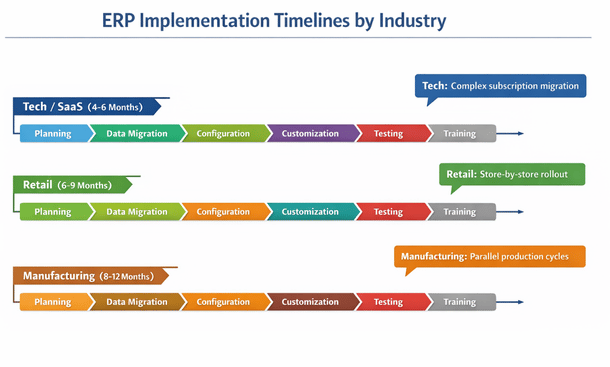
Different industries face distinct challenges during ERP customization implementation that require specific approaches.
Tech and SaaS companies often struggle with data migration from varied systems. Many startups cobble together QuickBooks, spreadsheets, Stripe, and homegrown databases before implementing a proper ERP. Consolidating this fragmented data requires custom extraction, transformation, and loading processes. Plan for data migration complexity and budget accordingly.
Retail implementations face the challenge of maintaining operations during cutover. You can’t shut down stores for days while implementing new systems. Retailers need phased rollouts, extensive parallel operation periods, and robust rollback plans. Pilot implementations at a single location before rolling out chain-wide reduce risk.
Manufacturing implementations must coordinate with production schedules. Cutover during a slow period minimizes disruption. Some manufacturers run old and new systems parallel for complete production cycles to ensure nothing falls through the cracks. Testing with real production orders and materials prevents surprises when go-live happens.
Change management requirements vary significantly by industry. Tech workers generally embrace new technology more readily than traditional manufacturing or retail workers. Training approaches must match employee demographics and technical comfort levels. Retailers might need simpler, more visual training materials. Manufacturers might need hands-on practice in mock production environments.
Integration testing complexity differs across industries. Tech companies might integrate with dozens of cloud services requiring extensive API testing. Retailers need to test POS systems, payment processors, and e-commerce platforms. Manufacturers test MES systems, industrial equipment, and quality devices. Industry-specific integration ecosystems drive testing scope and duration.
Compliance validation is critical for regulated industries. Healthcare manufacturers need 21 CFR Part 11 compliance validation. Public companies need SOX controls testing. Food distributors need FSMA compliance verification. Budget time and resources for compliance-focused testing and documentation beyond functional testing.
Support models post-implementation should reflect industry operational patterns. Retail businesses need weekend and evening support when stores are open. Manufacturing 24/7 operations might need around-the-clock support. Tech companies with standard business hours might accept normal support schedules. Match support availability to operational requirements.
Building Your Industry-Specific Strategy
Creating a comprehensive industry-specific customization strategy requires combining industry best practices with your unique business needs.
Start with an industry baseline of must-have customizations. Research what businesses in your sector typically implement. These form your minimum viable customization scope—the features you need just to operate competitively in your industry.
Layer on customizations that support your specific competitive strategy. If you’re pursuing operational excellence, focus on efficiency and cost-reduction customizations. If you’re emphasizing customer intimacy, prioritize customer portal and service quality features. If you’re driving product leadership, invest in innovation-supporting capabilities.
Build a three-year roadmap showing evolution from foundational customizations through advanced capabilities. Year one might focus on operational basics and compliance requirements. Year two adds efficiency improvements and better analytics. Year three implements sophisticated automation and competitive differentiators.
Create measurable success criteria for each customization. Don’t just implement features—define what success looks like. Subscription billing customization should reduce billing errors by ninety percent. Retail allocation customization should improve sell-through rates by fifteen percent. Manufacturing quality customization should reduce defect rates by thirty percent. Quantified targets focus implementation and enable measurement.
Budget realistically for industry-specific complexity. Highly regulated industries face higher costs due to compliance requirements. Industries with complex operational processes need more sophisticated customizations. Don’t use generic cost estimates—use industry-specific benchmarks from similar businesses.
Partner with industry specialists who understand your sector deeply. The consultant who knows retail inside and out delivers more value than the generalist who’s never implemented for a retailer. Industry expertise accelerates implementation, improves solution quality, and reduces risk.
Plan for ongoing evolution as your industry changes. New regulations, competitive pressures, and technological innovations constantly shift industry requirements. Budget for continuous customization enhancement, not just initial implementation. Your ERP customization strategy should be a living roadmap, not a one-time project.
Ready to dive deeper into making smart customization decisions? Our article on How to Choose the Right ERP Customization Partner shares critical guidelines for implementation success. And for comprehensive guidance on building your complete strategy, check out our full guide on tailoring your system to your business needs.
Industry-specific customization transforms your ERP from a generic business system into a competitive weapon optimized for how your sector operates. Invest the time to understand what matters in your industry, and your customizations will deliver compounding returns for years.
Did you find this helpful?
Your feedback helps us curate better content for the community.