Table of Contents
- User Interface and Experience Customization
- Workflow Automation and Business Logic
- Third-Party System Integrations
- Custom Reporting and Analytics
- Module Extensions and New Functionality
- Choosing the Right Type for Your Business
- Moving Forward With Your Customization Plan
Alright, so you know customization matters, but what exactly can you customize in an ERP system? The answer? Pretty much everything. There are five major categories of ERP customization that entrepreneurs typically explore: user interface modifications, workflow automation, third-party integrations, custom reporting, and module extensions. Each type serves different business needs and comes with its own investment level. Understanding these categories is crucial when you’re planning how to tailor your system to your business requirements. Let’s dive into each type so you can figure out what makes sense for your operation.
User Interface and Experience Customization
UI customization is all about making your ERP look, feel, and function in ways that match how your team actually works. This is often the most visible type of customization because it directly affects what users see and interact with every single day.
The simplest UI customizations involve dashboard personalization. Different roles need different information front and center. Your sales team wants pipeline visibility and customer interaction history. Your operations folks need inventory levels and fulfillment status. Your finance team cares about cash position and aging receivables. Custom dashboards put the right data in front of the right people without making them hunt through dozens of menu options.
Field customization takes this further by adding, removing, or rearranging data fields on forms and screens. Maybe the standard customer record has twenty fields, but your business only uses twelve of them while needing five additional ones that aren’t included. Customizing these forms reduces clutter and ensures your team captures the specific information that matters to your business model.

Navigation customization streamlines how users move through the system. Standard ERP platforms often have complex menu structures designed to accommodate every possible feature. By customizing navigation menus to show only the functions your team uses regularly, you eliminate confusion and speed up common tasks. Some businesses even create role-based navigation where warehouse staff see completely different menu options than accounting staff.
Branding customization might seem superficial, but it actually matters for user adoption. When your ERP includes your company logo, uses your brand colors, and feels like part of your business ecosystem rather than some foreign corporate software, employees engage with it more naturally. This psychological aspect of customization shouldn’t be underestimated.
The investment level for UI customization varies widely. Simple dashboard rearrangements and field additions might be something you can handle through built-in configuration tools without any coding. More complex interface redesigns typically require working with a developer or implementation partner, but the costs are usually moderate compared to other customization types.
Workflow Automation and Business Logic
This is where ERP customization gets really powerful. Workflow automation builds your business rules directly into the system so decisions and processes happen automatically instead of relying on manual coordination and tribal knowledge.
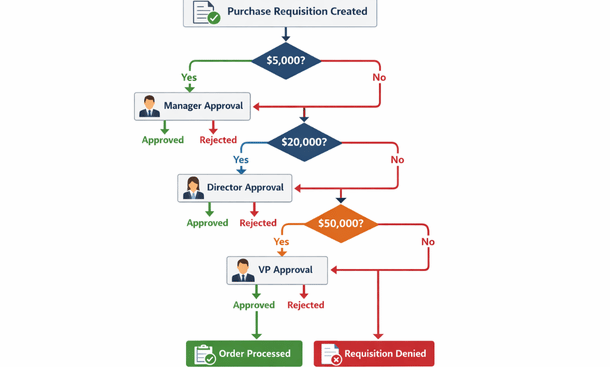
Approval workflows are probably the most common example. Let’s say your company requires manager approval for any purchase order over five thousand dollars, director approval over twenty thousand, and VP approval over fifty thousand. You can build this logic into your ERP so purchase requisitions automatically route to the right approvers based on dollar amount. The system tracks who’s approved what, sends reminders for pending approvals, and blocks orders from processing until they clear all necessary checkpoints.
Status-based automation triggers actions when records reach certain states. When a sales order moves to “ready to ship” status, the system might automatically generate picking lists, notify the warehouse team, reserve inventory, and create a preliminary shipping label. When an invoice gets marked as paid, it might trigger thank-you emails, update customer credit limits, and post entries to your general ledger. These cascading automations eliminate dozens of manual steps that used to require coordination across departments.
Calculation automation handles complex business logic that would otherwise require manual computation. Commission calculations are a perfect example. If your commission structure considers product categories, customer tiers, quarterly targets, and team versus individual performance, that’s incredibly tedious to calculate manually. Building those rules into your ERP means accurate commission numbers generate automatically with every sale.
Notification automation keeps everyone informed without manual communication. When inventory drops below reorder points, purchasing gets alerted. When customer payments are overdue, account managers receive notifications. When production runs complete, quality control gets pinged for inspection. These automated notifications ensure nothing falls through the cracks even as your operation grows.
The ROI on workflow automation is usually substantial because it compounds across every transaction. If you process a hundred orders per day and automation saves fifteen minutes per order, you’re talking about twenty-five hours saved daily. That adds up to real money and lets your team focus on higher-value activities instead of administrative busywork.
Third-Party System Integrations
Your ERP doesn’t exist in a vacuum. Most businesses run multiple software systems that need to communicate with each other. Integration customization builds bridges between your ERP and other platforms so data flows automatically instead of requiring manual export-import routines or duplicate data entry.
E-commerce integration is huge for retail and direct-to-consumer businesses. When someone places an order on your website, that order should automatically flow into your ERP, trigger inventory reservation, generate picking instructions, and update your accounting records. When inventory levels change in your ERP, those updates should push back to your website so you’re not selling products you don’t have. Bi-directional sync keeps everything aligned in real time.
CRM integration connects your customer relationship management system with your ERP for a complete view of each customer. Sales activity, support tickets, and marketing interactions from your CRM combine with order history, payment records, and shipping information from your ERP. This unified view helps both sales and service teams deliver better experiences because they have complete context.
Shipping carrier integration automates logistics workflows. Instead of manually entering shipment details on FedEx or UPS websites, your ERP pushes that data automatically, retrieves tracking numbers, generates labels, and sends tracking notifications to customers. For businesses shipping dozens or hundreds of packages daily, this integration saves hours and reduces errors.
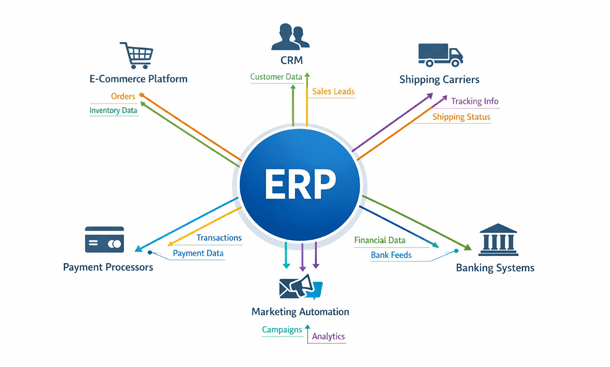
Payment processor integration streamlines financial operations. When customers pay via credit card, ACH, or digital wallets, those transactions post automatically to your ERP, match against open invoices, and update customer account balances. This eliminates manual payment entry and accelerates your cash application process.
Banking integration pulls transaction data directly from your business bank accounts into your ERP for automatic reconciliation. Instead of manually matching bank statement lines to internal records, the system does it automatically for straightforward transactions and flags exceptions for human review.
The complexity and cost of integration customizations depend heavily on the platforms involved. Systems with modern APIs and pre-built connectors are relatively straightforward. Legacy systems or platforms with limited integration capabilities require more custom development work and ongoing maintenance.
Custom Reporting and Analytics
Standard ERP reports rarely show exactly what you need to see. Custom reporting lets you build analyses that surface the specific insights driving your business decisions.
Operational dashboards provide real-time visibility into key metrics. A fulfillment dashboard might show orders pending processing, items picked today versus target, shipping accuracy rate, and average time from order to ship. A purchasing dashboard could display open purchase orders by supplier, items below reorder point, average vendor lead times, and spending trends by category. These live dashboards replace manual status meetings and spreadsheet updates.
Financial reports customized to your structure match how you actually think about your business. If you run multiple divisions or locations, you might need consolidated P&Ls that roll up in specific ways. If you bill by project or engagement, you need profitability reporting at that level of granularity. Custom financial reports ensure your accounting system tells you what you actually need to know.
Customer analytics combine transaction data with behavioral patterns to identify opportunities. Which customers have high lifetime value but decreasing order frequency? Which products are frequently bought together? What’s the typical path from first order to becoming a repeat customer? These insights inform marketing, sales, and product strategies.
Forecasting and planning reports use historical data to project future needs. Inventory forecasting might analyze seasonal patterns, growth trends, and lead times to recommend optimal stock levels. Revenue forecasting could combine pipeline data with historical win rates and average deal sizes to predict quarterly performance.
Exception reports automatically flag issues requiring attention. Items that haven’t moved in six months. Vendors with unusual price increases. Customers with declining order values. Projects trending over budget. These alerts let you manage by exception rather than reviewing everything manually.
The beauty of custom reporting is that once built, reports run automatically without ongoing effort. The initial investment in development pays dividends every single time someone uses the report to make a faster, better-informed decision.
Module Extensions and New Functionality
Sometimes the customization you need isn’t modifying what exists—it’s adding something entirely new. Module extensions create capabilities that weren’t part of your original ERP system.
Industry-specific modules address unique requirements of your vertical. A field service module for businesses dispatching technicians might include GPS tracking, mobile job completion forms, and parts usage capture. A quality management module for manufacturers could handle inspection protocols, non-conformance tracking, and corrective action workflows. These specialized modules plug into your core ERP while addressing needs that general-purpose software doesn’t handle.
Customer portal extensions give your clients direct access to relevant information. Instead of fielding calls about order status or invoice copies, you provide a portal where customers log in to see their information anytime. They can track shipments, download documents, review order history, and even place new orders directly. This reduces your support burden while improving customer experience.
Vendor portal extensions do the same thing on the supply side. Suppliers can view purchase orders, submit invoices, update shipping information, and access your specifications or quality requirements. This bidirectional visibility speeds up procurement cycles and reduces miscommunication.
Mobile extensions bring ERP functionality to smartphones and tablets. Warehouse staff can perform cycle counts, receive inventory, and pick orders from mobile devices instead of being tethered to desktop terminals. Sales reps can access customer information, check product availability, and enter orders from anywhere. Field technicians can view job details, record time, and capture customer signatures on-site.
Document management extensions organize all the files related to your business processes. Quotes, contracts, specifications, certifications, correspondence—everything lives within your ERP linked to relevant records. This eliminates the folder chaos of network drives and ensures everyone accesses current versions of important documents.
Module extensions typically represent the highest investment level among customization types because you’re building net-new functionality. However, they also often deliver the most dramatic operational improvements because they enable entirely new ways of working.
Choosing the Right Type for Your Business
So how do you decide which customization types matter most for your situation? Start by identifying your biggest operational pain points. Where does work get bottlenecked? What processes require excessive manual effort? Where do errors occur most frequently?
UI customization should be your starting point if user adoption is a challenge. If your team struggles to find information or complains about the system being confusing, improving the interface delivers quick wins that build momentum for larger changes.
Workflow automation makes sense when you have high-volume processes with consistent business rules. The more transactions you process, the faster automation pays for itself through time savings and error reduction.
Integration customization is critical if you’re currently doing manual data transfer between systems. Duplicate entry isn’t just time-consuming—it’s error-prone and makes your data less trustworthy.
Custom reporting matters most when decisions are delayed or made with incomplete information. If your leadership team is constantly requesting special analyses or your staff is spending hours building spreadsheets, reporting customization delivers immediate value.
Module extensions are the right choice when core functionality gaps prevent you from operating efficiently. If you’re using workarounds that involve separate systems or manual processes for key business functions, an extension brings everything under one roof.
Most businesses end up implementing multiple customization types over time. The key is sequencing them strategically so early wins fund later investments and your team isn’t overwhelmed by too much change at once.
Moving Forward With Your Customization Plan
Understanding these five customization types gives you a framework for evaluating what your business actually needs. The worst approach is customizing randomly based on whatever pain point is loudest at the moment. The best approach is stepping back, assessing your operation holistically, and building a prioritized roadmap that addresses high-impact opportunities first.
Think about how different customization types might work together. A customer portal extension becomes more valuable when combined with custom reporting that shows customers relevant analytics. Workflow automation delivers more benefit when paired with integrations that eliminate manual data bridges between systems.
Also consider your team’s ability to maintain customizations over time. Some modifications require ongoing attention, especially when your ERP vendor releases updates. Others are essentially set-and-forget. Factor maintenance requirements into your prioritization alongside implementation costs and expected benefits.
Ready to dig deeper into making smart customization decisions? Our article on ERP customization versus configuration breaks down when to use built-in settings versus custom development. And if you want comprehensive guidance on building your customization strategy, check out our complete guide on tailoring your system to your business.
The right mix of customizations transforms your ERP from a generic tool into a competitive advantage. Take the time to understand what’s possible, and you’ll make choices that compound benefits across your entire operation for years to come.
Did you find this helpful?
Your feedback helps us curate better content for the community.

